Understanding the concept of Mutual funds and how it help in your investments
Table of Contents
Let’s be honest—managing money can be overwhelming at times. Between paying bills, saving for the future, and trying to have a little fun along the way, you tend to push the idea of investing to the side.
But what if there was an easier way to grow your wealth without having to continuously track the stock market or become a finance expert? Presenting mutual funds: a simple, stress-free way for people to invest.
Think of mutual funds as a potluck dinner—everyone contributes a little something, and together you get to enjoy a variety of options, all chosen and managed by a fund manager. Meaning, instead of buying individual stocks and bonds on your own, you pool your money with other investors, and the fund manager does the heavy lifting, deciding where to invest to help you reach your financial goals.
Ready to dive in and learn more? Let’s break it down!
So, why should you learn about mutual funds?
Simply put, it helps in making informed investment decisions. It helps investors diversify portfolios and reduce risks, thereby helping to achieve long-term financial goals. Being informed will also help you in selecting the right type of fund based on your risk tolerance and investment horizon.
Let’s explore more and look at the different types of mutual funds. Just like how everyone’s financial goals and risk tolerance vary, there’s a mutual fund for every kind of investor. For instance, blue chip mutual funds are ideal for those who want to invest in stable, well-established companies with a strong track record.
Here’s a quick breakdown:
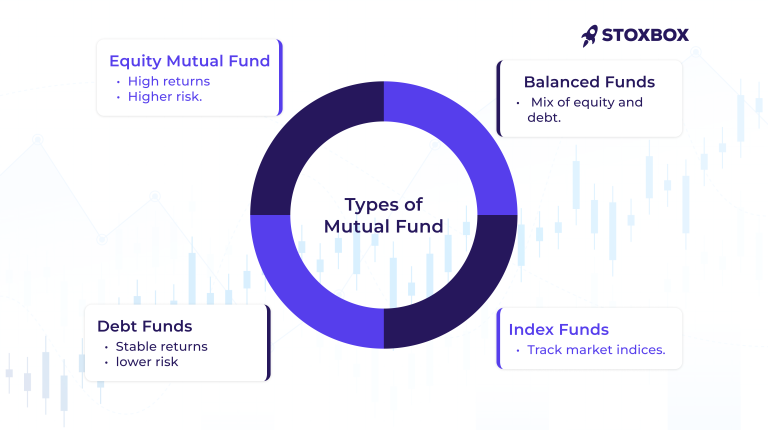
- Equity Mutual Funds: These funds invest primarily in stocks. If you’re looking for higher returns and don’t mind taking on a bit of risk, equity funds might be your speed—as stock markets can be volatile. Over the long term, equity mutual funds can offer substantial returns and can often beat inflation. In India, you can look at large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap funds, each targeting companies of different sizes. Equity mutual funds also come in various types. There are growth funds that focus mostly on capital appreciation, and then there are dividend yield funds that aim to provide regular income through dividends. You can also explore Flexi Cap Fund, which allows investment across various market capitalizations for a balanced approach.
- Debt Mutual Funds: If stability and lower risk sound more appealing, debt funds might be what you’re after. These invest in fixed-income securities like bonds, government securities, and corporate debt. These are suitable for those who have short-to-medium term investment horizons. The main goal is to preserve capital while producing a consistent income. The income stream comes through interest payments, and investors should be aware of the interest rates while investing. In India, liquid, short-term, and income funds are a few types of debt mutual funds.
- Balanced or Hybrid Funds: This gives you the best of both worlds. Balanced or hybrid funds invest in a mix of equities and fixed-income securities to balance risk and return. These funds are designed for investors who seek a moderate risk level—offering growth potential through equity while still providing some level of stability through the debt component. Aggressive hybrid funds, with a higher exposure to equities, and conservative hybrid funds, which lean towards debt, are popular balanced fund options in India.
- Index Funds: If you want to keep things simple and cost-effective, index funds are worth a look. They aim to match the performance of a specific market index (such as the Nifty 50) instead of trying to beat it. These funds offer low-cost exposure to the market by holding the same securities in the same proportions as the index they track. Index funds are passively managed, meaning they do not require active stock picking by fund managers, resulting in lower fees. Index funds are more predictable and cheaper than mutual funds. In India, popular index funds include those tracking the Nifty 50 and the Sensex.
- Sector Funds: These funds focus on a specific industry or sector, like technology, healthcare, or energy. Sector funds are great if you’re confident about a particular industry’s future and want to concentrate your investment in it. However, the risk can be higher, as your returns depend on how that sector performs. For instance, technology sector funds in India may benefit from rapid advancements but also face risks like regulatory changes. Investing in sector funds is most appropriate for those who have a higher risk tolerance and a strong belief in the growth potential of a particular industry.
- Tax-Saving Funds (ELSS): Tax-saving funds, or Equity Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS), offer tax benefits under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act. These funds invest primarily in equities and have a lock-in period of three years, which also gives them time to grow. You can claim a deduction of up to ₹1.5 lakh in a financial year, making it a popular choice for tax-conscious investors. ELSS funds are well liked in India by investors who want to lower their taxable income and possibly increase their returns. Axis Long Term Equity Fund and Mirae Asset Tax Saver Fund are two examples of ELSS funds. These funds are suitable for investors with a long-term investment horizon and a higher risk tolerance.
Investing in SIPs (Systematic Investment Plans) is a popular way to start with mutual funds. If you’re wondering how to invest in SIP, it’s simple: you can begin with small amounts, making it accessible for all income levels. This approach enables consistent investing over time, helping to mitigate market volatility.
Risk vs. Reward in Mutual Funds
Investing in mutual funds is all about finding the right balance between risk and reward, depending on your financial goals. If you’re looking for higher returns and don’t mind taking on some risk, equity mutual funds could be a good fit. These funds primarily invest in stocks, which means they have the potential for significant growth—but with that comes higher volatility. They’re best suited for investors with a higher risk tolerance who are in it for the long haul.
On the flip side, if stability and lower risk are your priorities, debt mutual funds might be more your style. These funds invest in fixed-income securities like bonds, offering more predictable, steady returns. While you won’t see the same big gains as equity funds, debt funds are great for conservative investors focused on preserving capital and generating reliable income.
It’s also helpful to pay attention to some key metrics when choosing mutual funds, like the expense ratio, which tells you how much you’re paying to manage the fund, and the Sharpe ratio, which measures the fund’s performance relative to its risk. These tools can help you make more informed decisions and get the most out of your investment. Knowing what is xirr in mutual fund investments helps evaluate returns for irregular cash flows, making it a useful tool for assessing long-term performance.
Now that we have a basic idea about what mutual funds are, let’s see the advantages of investing in mutual funds.
- Diversification: This is one of the key benefits of investing in mutual funds. When you spread investments across various asset classes, sectors, and geographies, it reduces the risk associated with any single investment. For instance, if one stock in a mutual fund’s portfolio underperforms, other potentially profitable investments offset the overall effect on the portfolio. This makes them a safer choice compared to single investments like stocks or bonds.
- Professional Management: Fund managers use their expertise and resources to analyze market trends, research companies, and take informed decisions. This professional oversight ensures that the investor achieves the best possible returns within the fund’s investment objectives. You benefit from the experience and knowledge of these managers without needing to actively manage them yourself.
- Liquidity: This refers to how easy it is to buy or sell mutual fund investments. Due to their high liquidity, mutual funds allow investors to redeem their units at any time at the fund’s net asset value (NAV), usually at the end of each trading day. Mutual funds are also convenient and flexible because investors are mostly not locked into long-term commitments. For those who might need quick access to their money, this makes it a desirable option.
- Affordability: Mutual funds allow investors to start with small amounts, making them accessible to a broad audience. By allowing investors to make small, consistent contributions over time, Systematic Investment Plans (SIPs) make it more affordable. It helps in building a substantial investment portfolio gradually.
- Tax Benefits: One of the best features of some mutual funds, such as Equity Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS), is the tax benefit. ELSS funds offer tax deductions under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act, allowing investors to reduce their taxable income by up to Rs. 1.5 lakh annually. For tax-saving purposes as well as capital growth through equity investments, this makes ELSS an attractive option. There is also a three-year lock-in period, the shortest among tax-saving instruments.
How to Choose the Right Mutual Fund
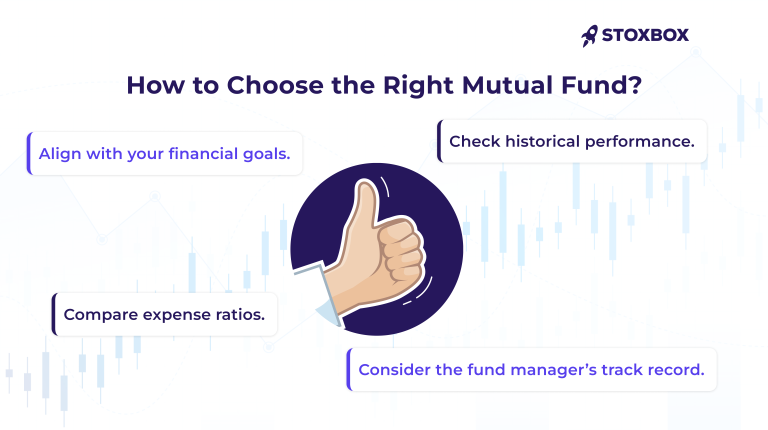
Picking the right mutual fund comes down to knowing what you want. Let’s break down the key things to look for so you can pick a fund that fits your goals perfectly.
- Investment Objective: When choosing a mutual fund, the first step is to see the fund’s objectives so that they are aligned with your financial goals. Each mutual fund has a specific objective, such as capital appreciation, income generation, or a balance of both. For instance, if you are saving for retirement, you might opt for a growth mutual fund focused on long-term capital appreciation. On the other hand, if you need regular income, a debt mutual fund may be more suitable.
- Performance: See how a mutual fund has performed historically—it helps in evaluating its potential. Past performance is not a guarantee of future results, but it provides insight into how the fund has managed market fluctuations and economic cycles. To get a full picture when comparing mutual funds, consider performance over a range of time periods, like one, three, and five years. Also compare the fund’s performance to its benchmark index and peers to measure its relative success.
- Expense Ratio: The expense ratio is a percentage of average assets in a mutual fund that indicates how much it costs to manage the fund. A lower expense ratio means that more of your money is being invested rather than used to cover management fees. When selecting a mutual fund, compare expense ratios to ensure you are getting the best value. For instance, index funds are often more affordable for many investors than actively managed funds because they have lower expense ratios.
- Fund Manager’s Track Record: The fund manager’s track record is a critical factor in a mutual fund’s performance. A skilled manager with a proven history of making sound investment decisions can impact your returns. Do your research on the manager’s experience, investment style, and performance across different market conditions to make sure that your investments are in capable hands.
- Risk: When selecting mutual funds, assessing risk is crucial. Different funds come with different levels of risk—from high-risk equity funds to low-risk debt funds. You should determine your investment horizon and risk tolerance, and then choose the kind that best aligns with your goals. There are several mutual funds investment plans available that cater to specific financial goals, timelines and risk appetites, making it easier for you to find the right fit.
We’ve looked at mutual funds from multiple angles. Now, let’s cover: how to Invest in mutual funds? There are a couple of steps, and we’ll go through all of them in detail.
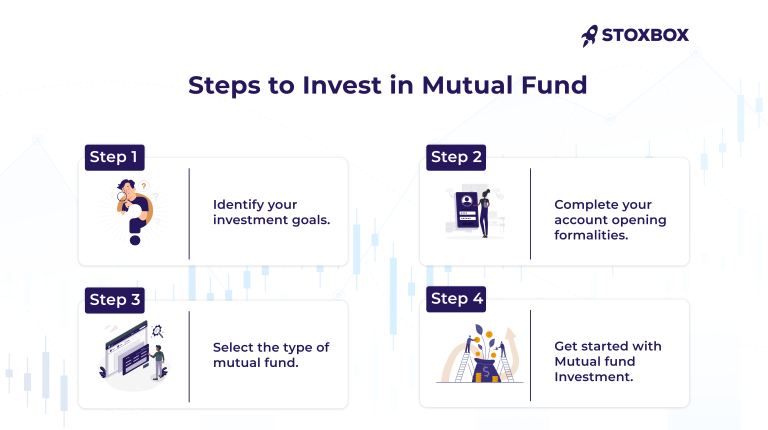
Step 1: Identify goals. The first step in investing in mutual funds is to identify your investment goals and define your time horizon. Knowing what you are trying to achieve with your investments—whether saving for retirement, buying a house, or funding education—will help you choose the right kind to invest in. Your time horizon, the period you are going to stay in this investment, also dictates which kind of mutual fund you will choose.
Step 2: Choose the type of fund. Once you have identified your goals, the next step is to choose the type of mutual fund that matches them. Each type of fund has different risk and return profiles. As we’ve seen, equity mutual funds are suitable for investors looking for high returns and who can tolerate higher risk. Debt mutual funds are ideal for conservative investors seeking stable returns.
Step 3: KYC Compliance. Before you can start investing, you need to complete KYC (Know Your Customer) compliance. This step is mandatory for all investors in India and involves submitting documents such as proof of identity, proof of address, and a recent photograph. KYC compliance ensures that transactions made in mutual funds are safe and recognised under law. This can be done online through KYC Registration Agencies (KRAs) or offline by visiting mutual fund offices.
Step 4: Select a platform. To invest in mutual funds, you need to select a platform. You can choose to invest through a broker, a mutual fund house, or an online investment platform. Each option offers different advantages. Brokers provide personalized advice and support, while mutual fund houses offer direct plans with lower expense ratios. Online platforms are convenient and provide easy access to a wide range of funds.
Step 5: Invest. The final step is to start investing. There are two ways to do this—making a lump sum investment or by setting up a Systematic Investment Plan (SIP). SIPs make it easy to invest small amounts on a regular basis, which is perfect for gradually increasing your wealth without putting a strain on your finances.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
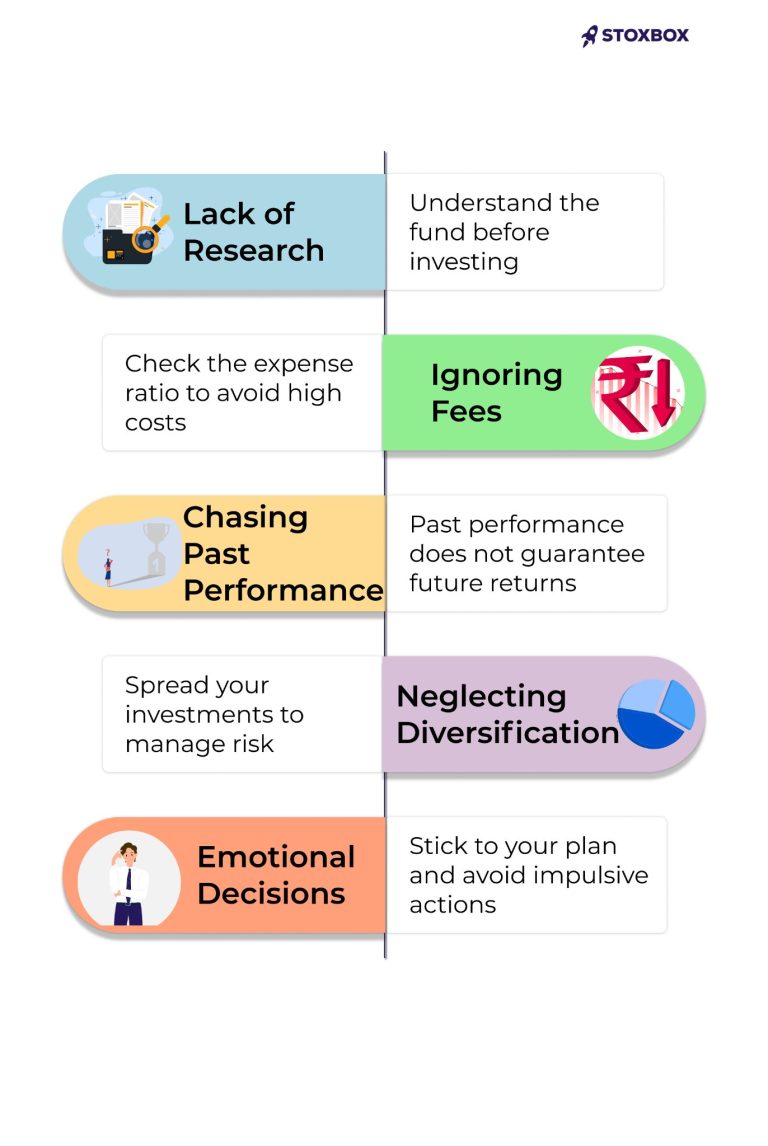
- Lack of Research: One of the most common mistakes investors make is not doing enough research before investing in mutual funds. It is possible that the funds you select will not fit your risk tolerance or financial objectives. Research means studying the fund’s historical performance, investment strategy, and the credibility of the fund manager. If you don’t do enough research, you risk investing in funds that may not provide the expected returns.
- Ignoring Fees: Ignoring fees, such as the expense ratio, is another common mistake. Your overall returns are directly impacted by the expense ratio, which is the annual fee the fund charges to manage your investments. Higher expense ratios can eat into your profits, especially over the long term. When comparing mutual funds, always consider the expense ratio and opt for funds with lower fees to maximize your returns.
- Chasing Past Performance: Many investors assume that a fund’s historical success will continue indefinitely. While past performance can provide some insight into a fund’s management and strategy, it does not guarantee future results. Fund performance is affected by shifting economic and market conditions. Instead of relying solely on past performance, consider other factors like the fund’s consistency, investment approach, and risk management.
- Neglecting Diversification: Investors often put all their money into one fund or asset class—this is a mistake. Diversification plays a crucial role in risk control and helps in stable returns. To lessen the effects of a bad performance in a particular fund, spread your investments across a variety of asset classes.
- Emotional Decisions: Making emotional decisions based on market fluctuations tends to be really bad for your investment strategy. People panic and sell their holdings when the market goes down, only to buy them back at higher prices when the market recovers. Instead, it’s essential to stick to a well-thought-out investment plan and avoid impulsive decisions.
- Tax Implications of Mutual Fund Investments : Gains from mutual funds are taxed differently based on the type of fund and the holding period. In the case of equity mutual funds, if you hold the investment for more than one year, it is considered as long-term capital gains (LTCG). LTCG on equity funds exceeding Rs. 1 lakh in a financial year are taxed at 10% without the benefit of indexation. When the holding period is less than one year, then the gains become short-term capital gains (STCG) and are taxed at 15%.
For debt mutual funds, the tax treatment varies. If you hold debt funds for more than three years, the gains are considered long-term and are taxed at 20% after applying the benefit of indexation, which adjusts the purchase price for inflation. This reduces the taxable gain. Short-term gains from holdings less than three years are added to your income and taxed as per your applicable income tax slab.
We’ve covered almost everything about mutual funds! Ultimately, they offer an excellent way to grow your wealth without requiring you to be a financial wizard. You can aim for long-term growth or focus on steady income—there’s always a fund that fits your goals.
Consider using trading apps like Stoxbox, which offers a user-friendly platform with zero brokerage fees. It helps you track and manage your mutual fund investments easily, making your investment journey much simpler.
Your Wealth-Building Journey Starts Here

